
Google Blacklist – how to remove your website from Google Blacklist (when you use WordPress, Magento, PrestaShop, OpenCart, Drupal & PHP)
Is your website’s search results flagged with a notice suggesting it might be risky? Unfortunately, this indicates that your site has been added to Google’s blacklist. Websites compromised by hacking or infected with malware typically receive such alerts/warnings to protect users. This situation could negatively impact your credibility (and traffic also).
Facing the same issue? Then continue reading to discover the reasons behind Google’s blacklisting of your site and learn how to get it removed from this list.
What is Google blacklist and what is used for?
Google maintains a database known as the Google blacklist, which lists websites identified as harmful by Google or flagged by other search engines, or cybersecurity firms. These sites might be involved in distributing malware, executing phishing schemes, or spreading spam, and the blacklist serves to shield users from such threats.
Given that Google is the leading search engine globally, with millions of searches conducted daily, it plays a crucial role in guiding users to the information they seek. It indexes countless web pages, delivering those most relevant to the user’s query. With the responsibility of ensuring user safety, Google proactively seeks out and blocks access to websites that may pose a risk. This involves continuous scanning of web pages for malicious software, deceptive content, misleading redirects, and intrusive advertisements.
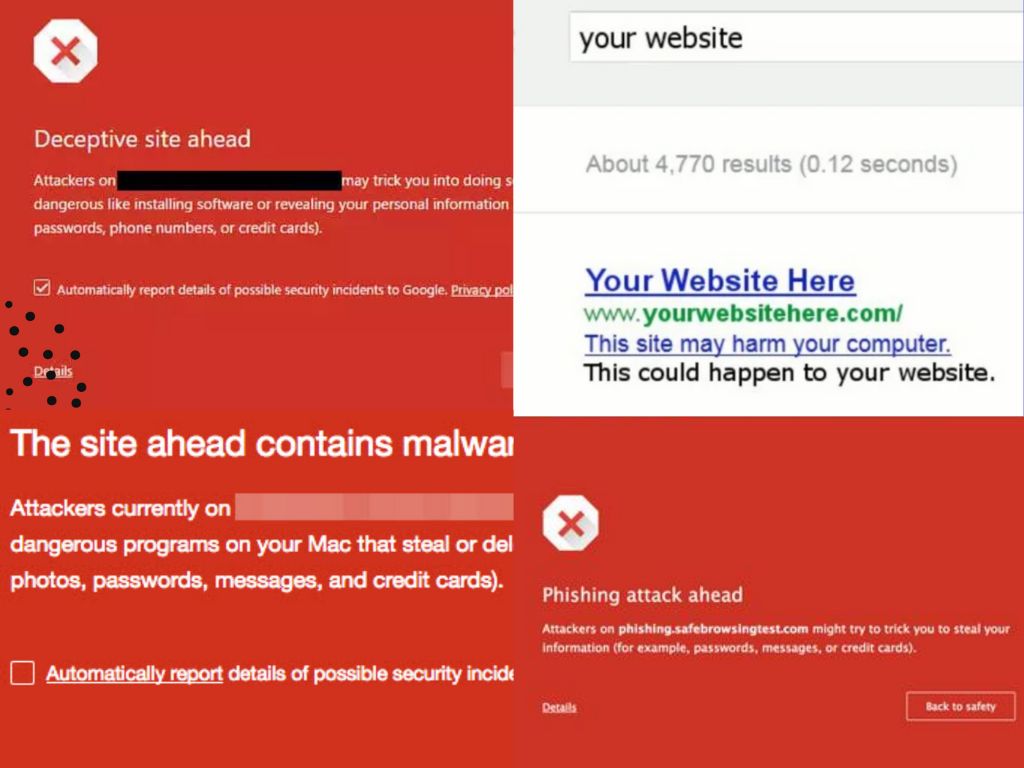
Whenever Google detects harmful content or files on a website that could jeopardize the security of its visitors, it triggers a Google blacklist warning for that site. Visitors are then greeted with a warning message from Google when they attempt to visit the site, which might read – ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’, ‘This website contains malware’, ‘This site has been hacked’, etc. Website owners are also alerted through an email or a notification in Google’s Search Console.
How does influence you/your website, when it is placed on Google’s blacklist?
What are the consequences of being placed on Google’s blacklist? Typically, two major actions occur when a website is blacklisted by Google:
- The website, or specific web pages, are removed from Google’s index. This means that if your site is blacklisted, it will no longer appear in Google’s search results.
- A warning message is displayed to deter users from accessing the site. Additionally, Google demotes malicious web pages from its top search results to minimize the risk of users inadvertently clicking on them.
Being blacklisted by Google could result in your website losing all its organic traffic from the search engine. For businesses that rely heavily on Google to attract potential customers, this could significantly affect sales and revenue.
How to determine if your website has been blacklisted by Google and other search engines?
Google typically resorts to blacklisting a website only as a final measure. Often, a website may be compromised for weeks before Google detects the malicious code, ultimately leading to its blacklisting.
Besides Google’s blacklist, your website can also be flagged on other platforms. For example, you can be put on McAfee’s blacklist, VirusTotal, AVG, and Avast blacklist. But that’s not the full list – you can be blacklisted by many other companies providing search engines/browsers/cybersecurity software. It just depends on how significant a problem it is for you. But generally speaking, when you are OK for McAfee, VirusTotal, AVG, and Avast – your site will probably not be flagged by any other companies’ malware/spam/phishing scan services.
Indicators that your website might be on a blacklist
How can you identify if Google has blacklisted your website? Look out for these common signs, indicators, and symptoms:
- Encountering a large warning screen that blocks access to your site.
- Finding external links on your website that contain SEO spam keywords, which redirect to search engine results pages (SERP) upon being clicked.
- Noticing unauthorized and suspicious modifications to your website’s database files or the emergence of new files containing harmful content.
- Having your antivirus software block access to parts of, or your entire website, during visits.
- Observing warnings like ‘This site may be hacked’ in your search engine results.
- Experiencing an unexpected suspension of your account by your hosting provider, which remains in effect until the malicious content is removed and the site is resubmitted for verification.
Why you can be blacklisted by Google – what can cause you to have been placed on Google blacklist?
Websites are constantly monitored by authorities such as Google, Bing, and McAfee SiteAdvisor for malware presence, which can range from trojan horses and pharma hacks to SEO spam and phishing schemes. To maintain their integrity and trustworthiness, search engines aim to protect users by blocking or restricting access to infected sites.
Often, website owners are unaware of a hack until they find out their site has been blacklisted by entities like Google.
Reasons for a website being blacklisted vary: some sites are flagged for hosting spam, others for containing malware, and some for featuring external links that lead to phishing scams, endangering data privacy and security. These scenarios typically lead to a website being blacklisted, necessitating detailed and accurate actions to restore its status.
Reasons for getting blacklisted by Google
Malware presence
Your website might end up on Google’s blacklist if it’s suspected of spreading malware. If any pages on your site have been compromised to automatically download malware upon visiting, Google will likely take notice, identifying your site as part of a widespread malware distribution effort.
To protect internet users, their browsers may show a warning when attempting to access your site, often displaying a message or a red screen with the word ‘malware’ on Chrome. Other browsers might issue various alerts, such as “This site may be hacked,” “This site may harm your computer,” or “deceptive site ahead.”
Seeing such warnings on your website should prompt immediate actions toward Google blacklist removal.
Phishing activities
Your site being marked as deceptive or fraudulent could stem from it being listed on Google’s phishing list. Hackers might have altered your website to harvest user information, redirecting it to servers under their control. These altered web pages could request sensitive details from users, putting those who comply at risk of being targeted. This not only compromises user trust but can also severely damage your site’s reputation.
Utilizing black hat SEO practices
Engaging in black hat SEO tactics, including cloaking, website scraping, and purchasing links for your website, might lead to Google blacklisting your site. These practices are considered unethical because they provide websites with an unfair advantage, prompting Google to monitor and penalize sites employing these methods.
Hosting malicious downloads
Websites offering downloads that contain malware, spyware, or any other type of malicious software can be blacklisted. Google aims to prevent the spread of harmful software that could damage users’ devices or compromise their data.
Suspicious redirections
Websites that redirect visitors to other, potentially harmful sites without their consent could be blacklisted. These redirections often lead to phishing sites, scam pages, or other malicious websites, undermining user trust and safety.
Spammy content
Websites filled with spammy content, such as irrelevant or excessive keywords, hidden text, and doorway pages, can be blacklisted. This content degrades the quality of search results and provides a poor user experience.
There are many other numerous other reasons why Google might blacklist a website, extending beyond the common issues of malware, phishing, and black hat SEO practices. For instance, websites that engage in link farming or have an excessively slow loading time due to unoptimized content could find themselves penalized (you are not on black list officially, but it still does affect your site). Additionally, sites with an abundance of intrusive pop-up ads, or those that are part of a network known for distributing spam, may also be at risk. Furthermore, any website found to be involved in social engineering tactics or exploiting browser vulnerabilities to install unwanted software without user consent could be blacklisted. Ending this section, it’s vital to recognize that Google’s overarching aim in imposing these penalties is to ensure a safe, trustworthy, and efficient internet environment for all users. Adhering to Google’s Webmaster Guidelines (now called Google Search Essentials) is the best practice for avoiding such penalties and maintaining a positive standing with the search engine.
Removing your site from Google’s blacklist
If you’ve determined that Google has blacklisted your site, immediate action is required to have it removed. Follow this step-by-step guide to get your website off the blacklist.
- Identifying the infection
- Eliminating infections/malware
- Requesting a blacklist removal review from Google
- Clearing your site’s IP from spam lists
Identifying the infection
Starting with the Google Search Console is a wise choice, as it can pinpoint the reason your site was blacklisted, whether due to malware, SQL injection, or spam link injection.
Understanding the specific reason provided by Google is crucial for effectively addressing and resolving the issue.
Identifying a website infection accurately requires a combination of vigilance, knowledge of common vulnerabilities, and the use of diagnostic tools. Here’s a more detailed approach to pinpointing the nature of the infection and some recommended free tools that can assist in this process:
Detailed website inspection process
- Google Search Console alerts: One of the first indicators of possible infection is a warning from the Google Search Console (formerly Webmaster Tools). Google scans websites for malicious content and will notify the site owner of potential security issues, including malware, phishing attempts, and unusual redirects.
- Manual code review: Manually reviewing your website’s code can be daunting but is necessary for identifying suspicious code snippets. Look for unfamiliar or obfuscated JavaScript, PHP, or HTML code, especially in the site’s header, footer, or .htaccess file.
- Check website behavior: Monitor your website for unexpected behavior, such as new pop-ups, redirected pages, or unauthorized ads. These can be signs of a hack or infection.
Free Diagnostic Tools
- Sucuri SiteCheck: Sucuri offers a free website scanner that can detect malware, website defacements, and signs of SPAM injections. It’s user-friendly and provides detailed reports on detected issues.
- Google Safe Browsing: Google’s Safe Browsing tool allows you to check if your website is currently listed as suspicious. Simply visit, replacing “yourdomain.com” with your actual domain name: http://www.google.com/safebrowsing/diagnostic?site=yourdomain.com
- VirusTotal – this tool aggregates multiple antivirus and website blacklisting services, providing a comprehensive check of your website for malicious content.
- Quttera – Quttera offers a free web scan tool that checks for malware, suspicious scripts, and exploits. It can also scan web applications for potential security vulnerabilities.
- Wordfence (for WordPress sites) – Wordfence includes an endpoint firewall and malware scanner designed specifically for WordPress. Its scanner checks core files, themes, and plugins for malware, bad URLs, backdoors, SEO spam, and other issues.
There are for sure many other tools and options for how to check your “website health check”. Just trying to describe what you should probably have to do and what the process could look like. That’s actually part of the know-how of the cybersecurity people on how to diagnose the problem precisely.
Additional steps
- Check file and directory permissions: Ensure that your file and directory permissions are set correctly. Incorrect permissions can be an invitation for attackers to exploit your website.
- Review user access logs: Access logs can reveal suspicious activity, such as repeated failed login attempts or unusual IP addresses accessing your admin pages.
Identifying the source of a website infection is the first critical step toward cleaning and securing your site. Utilizing these tools and strategies can significantly aid in detecting and understanding the scope of the compromise, allowing for more effective remediation efforts.
Removing infections
Upon identifying the infections, proceed with caution during the cleanup process to ensure thorough removal of vulnerabilities.
- Manually examine and delete any unauthorized changes on your site.
- Pay special attention to commonly targeted files by hackers, such as:
- The website’s index file (typically index.php), especially the header and footer for unusual code or text.
- The .htaccess file, which hackers might manipulate to redirect visitors to harmful sites, potentially leads to a blacklist by search engines.
- Critical WordPress files like functions and wp-config, contain sensitive information.
- Inspect key database tables for injected malicious scripts that could result in remote code execution or SQL injection. Important tables to review include those storing article content (like wp-posts), user details, and form submissions.
- Disable and remove plugins that are inactive but still installed on your site.
- Investigate for any unauthorized admin accounts, remove them, and update all login credentials.
- Manually cleanse infected database tables.
- Implement two-factor authentication for added security.
- Remove any unverified users added to the site without authorization.
Taking these steps not only aids in cleaning current infections but also fortifies your website against future attacks, helping to lift any blacklisting status and restore your site’s integrity.
Requesting a review for Google blacklist removal
After addressing the issues leading to your site’s blacklisting, you can request a malware review from Google to have your site removed from the blacklist. The review process might vary in duration, typically from a few hours up to a couple of days. Follow these steps to initiate a review:
- Navigate to the Security Issues tab in Google Search Console to examine the problems identified by Google.
- Click on “I have fixed these issues” to indicate that you have addressed the detected security concerns.
- Select “Request a Review” to start the review process.
- Provide a comprehensive description of the actions you undertook to eliminate malware from your site and resolve the reasons for its blacklisting. It’s crucial to include detailed information to facilitate the review process.
- Access the Manual Actions section to submit your review.
If your site had multiple issues, repeat steps 1 through 4 for each problem until you’ve requested a review for all resolved issues.
Removing your site’s IP from spam lists
How to avoid Google blacklist in the future? Well, there are a few procedures that can help you minimize the risk of being hacked or placed on the Google blacklist, but it still cannot guarantee 100 % certainty/assurance that you will never be hacked. It just limits the chance (but in most cases very drastically).
- Leverage Google Analytics – utilizing Google Analytics can provide deep insights into your website’s performance and traffic patterns. It’s an effective tool for detecting unusual activity that could indicate malware infection, offering valuable data to help safeguard your site.
- Adopt ethical SEO practices – reconsider the use of any black hat SEO tactics, as these are likely to land your site on Google’s blacklist. Instead, focus on ethical, or white hat, SEO strategies to enhance your website’s appeal, such as:
- Enhancing your website’s content to engage users longer.
- Ensuring your website’s security is robust.
- Catering to your visitors’ search intents and needs. Acting swiftly in case of blacklisting minimizes potential harm.
- Regular website updates – consistently updating your website’s software is crucial for security. This preventive measure is simple yet highly effective in protecting your site from vulnerabilities that could lead to being blacklisted. It’s vital to maintain the latest versions of plugins and web applications on your site. For those using third-party or lesser-known plugins, stay informed about updates through the developers’ social media channels or websites. For WordPress users, take advantage of the auto-update feature for plugins and themes to keep your site up to date effortlessly.
- Schedule a security audit – in today’s digital landscape, the security of your website cannot be overstated. A website that lacks robust security measures is at a higher risk of being blacklisted. Opting for a security audit can significantly enhance your website’s defenses. An expert assessment can elevate your website’s security from good to outstanding, identifying vulnerabilities and recommending actionable improvements.
- Implement a security solution – constantly monitoring your website for malware can be an exhaustive task. However, employing a security solution for example from us :-), can offer you continuous surveillance and protection against hackers and malware. By safeguarding your site with such a solution, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of being blacklisted by Google.
- Invest in secured rock-solid web hosting – every web hosting company should take security very seriously. The reason why it is essential that you choose a web host you can rely on for your business. It’s not just about uptime and support; it’s about ensuring that your data is protected against online threats. Ideally hosting company should implement CloudLinux across its servers, allowing for individualized virtual file systems that isolate each account for enhanced security. This means that even if one account is compromised, others on the same server remain unaffected. Plus additional hosting partnership with other security companies fortifies the whole hosting solutions with a multi-tiered defensive strategy to precisely target and eliminate malware and viruses, providing an additional layer of security over our competitors.
- Regular website backups are essential – consistently back up your website. This process involves duplicating your site’s data and storing it securely, so you have the option to restore your site if needed. Many hosting services offer automated backup solutions. Some hosting plans include free automated backups that are stored offsite, ensuring that you can quickly recover your data and have peace of mind.
- Implement CAPTCHAs – CAPTCHAs solutions are an effective barrier against bots attempting to misuse your site’s forms, such as contact submissions or comments. They help prevent malicious code submissions and maintain the integrity of your site.
- Smart username and password management – choosing a unique username and a complex password for your admin dashboard is a simple yet powerful security measure. Avoid common usernames like “admin” and opt for passwords that are difficult to guess. Tools like 1Password’s Password Generator can help create strong passwords. For those managing multiple sites, a password manager like 1Password, which offers a free tier, is ideal for keeping track of different logins securely.
- Turn off directory browsing – if a web server cannot locate an index file (like index.php or index.html), it often defaults to displaying a page listing all files and folders in the directory. This can inadvertently expose sensitive information and potentially give hackers the insights they need to exploit a weakness in a WordPress plugin, theme, or the server itself. To prevent this, simply insert the following directive into your website’s .htaccess file, which you’ll find in the site’s root directory:
Options -IndexesGood hosting companies already have the directory listings disabled on their servers by default. - Implement HTTPS with an SSL certificate – a commonly overlooked step in fortifying a WordPress site is implementing an SSL certificate to secure connections via HTTPS.At ChemiCloud, as with many hosting services, we provide complimentary SSL certificates through Let’s Encrypt, making it easier for you to secure your site.
Fixing Google warnings procedure/Fixing warning messages in Google
- Start with Google Search Console – navigate to the Security Tab within the console to examine alerts about potential security issues. This will clarify the type of security breach, such as malware, SQL injection, etc., and pinpoint the affected pages. Ensure you have verified ownership of the site if necessary.
- Inspect JavaScript files – utilize the ‘Inspect Element’ and ‘Google Developer Console’ to examine any third-party JavaScripts being loaded on your site. Employ online tools to check if these scripts are marked as harmful by Google.
- Utilize a Malware scanner – scan your website with a malware scanner that’s compatible with your CMS or technology stack to identify the specific malware and the files that have been compromised.
- Backup before making changes – always back up your entire website, like the public_html directory, before making any changes. This precaution allows you to restore original content if something legitimate is accidentally removed. Your hosting provider can assist with the backup process.
- Submit a review request – after cleaning your website, request a review through the Google Search Console. Detail the actions taken to eliminate the malware. Google typically confirms the review within 1-3 days.
Was this article helpful?
Support us to keep up the good work and to provide you even better content. Your donations will be used to help students get access to quality content for free and pay our contributors’ salaries, who work hard to create this website content! Thank you for all your support!

Reaction to comment: Cancel reply